CompTIA Security+ PBQs Explained (SY0-701): Types, Examples, and How to Prepare
Performance-Based Questions (PBQs) are the single most misunderstood—and most feared—component of the CompTIA Security+ (SY0-701) exam. Many otherwise well-prepared candidates report that PBQs feel “unexpected,” “overwhelming,” or “nothing like practice questions.”
That anxiety is understandable. PBQs look different, behave differently, and demand a different mindset than multiple-choice questions.
This guide exists to remove that uncertainty.
Rather than guessing what PBQs might look like, this article distills clear, recurring patterns based on official exam objectives and aggregated exam-taker experiences. You will learn what PBQs are testing, why they are designed the way they are, and how to approach them methodically on exam day.
Important note upfront:
CompTIA does not publish actual PBQs.
PBQs vary by exam form and candidate.
This guide identifies recurring PBQ types and skill patterns, not leaked or memorized questions.
1. Executive Summary
Performance-Based Questions (PBQs) are interactive, scenario-driven exam tasks that require candidates to apply security knowledge rather than recognize an answer.
In the Security+ exam, PBQs:
Test real-world cybersecurity reasoning
Commonly appear at the start of the exam
Require multi-step decision-making
Often consume more time than MCQs
In this guide, you will learn:
How PBQs differ fundamentally from multiple-choice questions
Why PBQs feel harder even when you “know the material”
The eight core PBQ categories repeatedly reported by candidates
A universal PBQ problem-solving framework
Realistic, conceptual PBQ walkthroughs
Practical 7-day, 14-day, and 30-day PBQ-focused study plans
The objective is not to “predict” questions—but to train the thinking patterns Security+ PBQs require.
2. What Are Performance-Based Questions (PBQs)?
Performance-Based Questions are designed to simulate job-task decision making rather than academic recall.
Instead of asking “Which of the following is best?”, PBQs ask:
Configure this securely
Identify what went wrong
Fix this misconfiguration
Choose the most appropriate control
How PBQs Differ from MCQs
Multiple-Choice Questions | Performance-Based Questions |
|---|---|
Recognition-based | Application-based |
One decision | Multiple interdependent decisions |
Clearly bounded answers | Open-ended problem space |
Fast to complete | Time-intensive |
Tests recall | Tests reasoning |
Common PBQ Interaction Styles
PBQs often appear as:
Simulated interfaces (firewalls, OS settings, wireless configs)
Drag-and-drop tasks (control placement, process ordering)
Log viewers (SIEM, firewall, endpoint logs)
Configuration panels (VPNs, authentication, encryption)
The interface is intentionally simplified, but the decision logic is real-world accurate.
3. Why PBQs Feel Harder Than Multiple-Choice Questions
PBQs feel harder for reasons that have little to do with intelligence or preparation quality.
1. Cognitive Load
PBQs require you to hold multiple constraints in your head simultaneously:
Security objective
Environment context
Available controls
Business impact
MCQs rarely demand this.
2. Multi-Step Reasoning
PBQs often require:
Identifying the problem
Diagnosing root cause
Selecting the correct control
Applying it correctly
Missing any step can result in partial or incorrect outcomes.
3. Tool-Like Interfaces
PBQs intentionally resemble:
Firewall consoles
System settings
Administrative dashboards
Candidates unfamiliar with how these tools behave may freeze, even if they know the theory.
4. Time Pressure
A single PBQ can take 5–15 minutes. Poor time allocation early can cascade into rushed decisions later.
4. Security+ Exam Context (SY0-701 Overview)
Understanding where PBQs come from helps demystify them.
Security+ SY0-701 Domains & Weights
Domain | Focus | Weight |
|---|---|---|
1. General Security Concepts | Foundations | 12% |
2. Threats & Vulnerabilities | Attacks & risks | 22% |
3. Security Architecture | Network & design | 18% |
4. Security Operations | Monitoring & response | 28% |
5. Security Program Management | Governance & risk | 20% |
Why PBQs Cluster in Certain Domains
PBQs overwhelmingly map to:
Domain 3 (Security Architecture)
Domain 4 (Security Operations)
These domains represent hands-on security work, making them ideal for simulation-based assessment.
6. The Core Types of PBQs Asked in the Security+ Exam
This is the most important section of the guide.
Each PBQ category below represents a recurring task pattern, not a single question.
6.1 Network Diagram & Security Control Placement

What the PBQ looks like
You are shown a network diagram with zones, servers, and traffic flows. You must place:
Firewalls
IDS/IPS sensors
DMZ boundaries
Segmentation controls
Skills being tested
Defense-in-depth
Trust boundary identification
Data flow reasoning
SY0-701 domain mapping
Domain 3: Security Architecture
Common mistakes
Placing databases in DMZs
Ignoring east-west traffic
Over-securing low-risk paths
Step-by-step strategy
Identify public vs internal assets
Trace inbound and outbound flows
Place controls at trust boundaries
Apply least privilege
How to practice
Draw simple network diagrams and explain your control placement out loud.
6.2 Firewall / ACL Rule Configuration
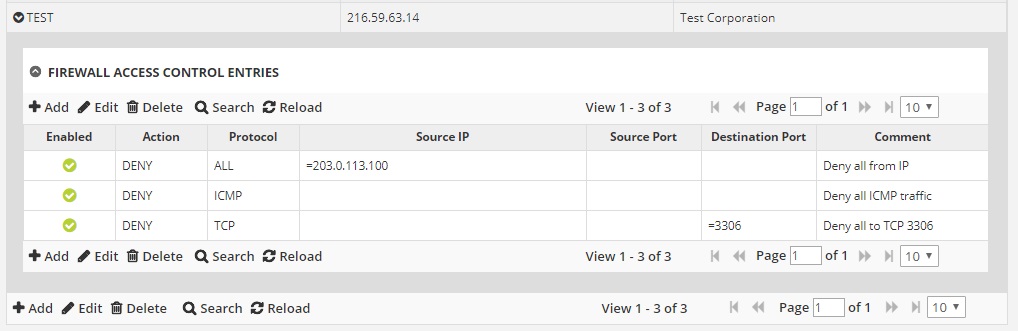
What the PBQ looks like
You configure allow/deny rules using:
IP addresses
Ports
Protocols
Skills being tested
Rule ordering
Port knowledge
Least privilege
Common mistakes
Using “any-any” rules
Incorrect protocol selection
Forgetting implicit deny
PBQ strategy
Translate requirements into plain English
Write narrow allow rules first
Confirm rule order
Practice drill
Manually write firewall rules for common services (HTTPS, DNS, SSH).
6.3 Log Analysis & Incident Response
What the PBQ looks like
You analyze logs to:
Identify an incident
Trace attacker movement
Determine impact
Skills being tested
Log correlation
Timeline analysis
Incident identification
Common mistakes
Reading line-by-line instead of pattern scanning
Ignoring timestamps
Failing to correlate multiple log sources
PBQ strategy
Identify anomalies first
Correlate by time and IP
Determine patient zero
6.4 Endpoint Hardening & Secure Configuration
What the PBQ looks like
You harden a workstation or server:
Disable services
Enforce authentication
Enable host firewalls
Skills being tested
Secure baselines
System hardening
Common mistakes
Over-hardening
Disabling required services
PBQ strategy
Secure without breaking functionality.
6.5 Identity & Access Management Troubleshooting
What the PBQ looks like
Users cannot access systems due to:
Group membership issues
Permission errors
Authentication failures
Skills being tested
RBAC
Least privilege
PBQ strategy
Check authorization before authentication.
6.6 Cryptography & Secure Communication Selection
What the PBQ looks like
Select encryption methods for:
VPNs
Data at rest
Data in transit
PBQ strategy
Prefer modern, strong defaults:
AES
SHA-256+
TLS 1.2+
6.7 Wireless Security Configuration
What the PBQ looks like
Configure wireless security:
WPA2/WPA3
Enterprise vs Personal
PBQ strategy
Match security strength to environment.
6.8 Vulnerability Prioritization & Remediation
What the PBQ looks like
Rank vulnerabilities based on risk.
PBQ strategy
Prioritize:
Internet-facing
Actively exploited
High-impact assets
7. Universal PBQ Strategy: Exam-Day Playbook
Read the prompt twice
Identify PBQ category
Plan before clicking
Apply least privilege
Verify changes
Skip if stuck
Return later
Never leave PBQs blank
8. Full PBQ Walkthrough Examples (Conceptual)
Below is a clear, exam-focused summary of the three PBQ examples, distilled to their core intent, skills tested, and takeaway lessons, suitable for quick revision.
Example PBQ 1: Securing a Branch Office Network
PBQ Type: Network Diagram & Firewall Rules
What the scenario tested
Correct placement of security controls (firewall, IDS, DMZ)
Firewall rule creation using least privilege
Isolation of internal assets from public-facing systems
Key tasks
Place the firewall between the Internet and internal networks (LAN + DMZ)
Place IDS to monitor DMZ web traffic
Allow only HTTPS (TCP 443) to the web server from Internet and LAN
Ensure the file server is inaccessible from DMZ and Internet
Core reasoning
Public services go in the DMZ, not the LAN
Only explicitly required ports should be opened
No DMZ → LAN access unless stated
Why wrong choices fail
Overly permissive rules (e.g., allow any-any)
Allowing HTTP when only HTTPS is required
Enabling DMZ access to internal file servers
Main takeaway
PBQs reward precise access control and correct security zoning, not “working but insecure” configurations.
Example PBQ 2: Malware Infection Investigation
PBQ Type: Log Analysis & Incident Response
What the scenario tested
Timeline analysis across multiple logs
Identifying patient zero (initial infection source)
Correlating endpoint and firewall data
Key tasks
Determine which workstation was infected first
Identify secondary infections
Recognize which systems were unaffected (if applicable)
Core reasoning
The earliest malware event indicates patient zero
Later detections suggest secondary spread
Firewall logs support infection timelines (outbound C2 traffic, lateral movement)
Why wrong choices fail
Ignoring timestamps
Assuming “quarantined” means “never infected”
Guessing without correlating logs
Main takeaway
Security+ log PBQs are about sequence and correlation, not reading every line.
Example PBQ 3: Configuring Secure Wi-Fi Access
PBQ Type: Wireless Security & IAM Configuration
What the scenario tested
Proper selection of wireless security modes
Understanding WPA2-Enterprise vs WPA2-Personal
Basic RADIUS-based authentication concepts
Key tasks
Configure a corporate SSID using WPA2-Enterprise with RADIUS
Configure a guest SSID using WPA2-Personal with a pre-shared key
Ensure guest network isolation from internal resources
Core reasoning
Enterprise users authenticate with individual credentials (802.1X/RADIUS)
Guests use a shared passphrase
Security mode must match the stated requirement exactly
Why wrong choices fail
Using WPA2-Personal instead of Enterprise for employees
Selecting WEP or Open networks
Failing to isolate guest traffic
Incorrect RADIUS details
Main takeaway
Wireless PBQs test your ability to match security controls to business requirements, not just “pick the strongest option.”
Overall Pattern Across All Three PBQs
Across all examples, Security+ PBQs consistently reward candidates who:
Read requirements carefully
Apply least privilege
Respect network boundaries
Use timelines and evidence logically
Avoid unnecessary or “extra” configuration
Big picture insight:
PBQs are not about perfection or deep tool expertise—they are about making correct, defensible security decisions under constraints.
9. How to Prepare for Security+ PBQs
Below is a clear, high-signal summary of the PBQ preparation plans, condensed for easy consumption while preserving intent and structure.
7-Day PBQ Crash Course (Last-Minute Focus)
Best for: Candidates whose exam is imminent and who need rapid PBQ confidence.
Core focus
Fast review of PBQ-heavy objectives
Repeated exposure to common PBQ types
Minimal theory, maximum practical reasoning
What you do
Review exam objectives with PBQ mindset
Practice network diagrams, firewall rules, logs, system hardening, IAM, and wireless
Complete at least one timed practice exam
Reinforce key facts (ports, crypto, IR steps)
Mentally rehearse PBQ problem-solving steps
Key takeaway
This plan prioritizes recognition of PBQ patterns and calm execution, not deep new learning.
14-Day PBQ-Focused Study Plan (Balanced & Structured)
Best for: Candidates with two weeks who want solid hands-on ability plus theory refresh.
Core focus
Week 1: Foundation + light labs
Week 2: Intensive PBQ drills + timed practice
What you do
Review all Security+ domains with a “could this be a PBQ?” mindset
Set up basic labs (VMs or online platforms)
Practice firewall rules, logs, endpoint hardening, IAM, crypto, and wireless configs
Take mid-point and final timed practice exams
Identify weak areas and fix them before exam week
Key takeaway
This plan builds confidence through repetition and integration, ensuring PBQs feel familiar, not intimidating.
30-Day PBQ-Focused Prep Plan (Deep Mastery)
Best for: Candidates who want maximum readiness and real-world skill development.
Core focus
Progressive learning → practice → refinement
Heavy hands-on lab work
Multiple full practice exams
Exam-day simulation and confidence building
What you do
Build a full lab environment (VMs, firewall, logs, tools)
Practice real security tasks: hardening systems, analyzing logs, configuring access
Run mini-projects (secure a system, simulate an attack and detection)
Drill each PBQ category individually
Take multiple full practice exams and correct weak spots
Develop PBQ checklists, cheat sheets, and mental playbooks
Gradually taper study to avoid burnout
Key takeaway
This plan transforms PBQs from an exam obstacle into a strength grounded in real skills.
Overall Comparison at a Glance
Plan | Time | Depth | Ideal Candidate |
|---|---|---|---|
7-Day | Very short | Tactical | Exam is days away |
14-Day | Moderate | Balanced | Needs practice + review |
30-Day | Long | Deep mastery | Wants full confidence |
Bottom Line
All three plans share the same principle:
PBQs are best prepared through structured thinking and hands-on practice, not memorization.
The difference is how much time you have to reinforce those skills.
If you want, I can:
Turn these summaries into a visual comparison table
Create a PBQ-only 14-day checklist
Adapt one plan specifically for FlashGenius users
Convert this into a downloadable study roadmap
Just let me know.
10. Common PBQ Mistakes That Cause Score Loss
Misreading requirements
Over-configuring
Ignoring rule order
Poor time management
Leaving PBQs unanswered
11. PBQ Readiness Checklist
Can interpret network diagrams
Can configure firewall rules
Can analyze logs confidently
Understands secure defaults
Has practiced under time pressure
12. FAQ About Security+ PBQs
How many PBQs are on the Security+ exam?
Most candidates see 3–5 PBQs. CompTIA caps the total exam at 90 questions (MCQs + PBQs combined). PBQs usually appear at the start of the exam.
Where do PBQs appear in the test?
They are typically presented first, before multiple-choice questions. While they could appear elsewhere, most reports confirm they’re front-loaded—so expect to start the exam with PBQs.
Can PBQs be skipped and revisited later?
Yes. On Security+ SY0-701, PBQs are simulation-based and can be skipped, flagged, and revisited, with your work saved. (Non-returnable lab-style PBQs are not used in this exam.)
How are PBQs scored?
Exact scoring is undisclosed, but:
Partial credit is possible
PBQs may be worth more than MCQs
Some questions (MCQ or PBQ) may be unscored trial items
Treat every PBQ as scored and complete as much as you can.
What if I can’t finish a PBQ completely?
Do as much as you know, then move on. Partial credit is better than zero. Don’t sacrifice many MCQs to perfect one PBQ—time management matters.
Can I see real PBQ examples?
No real exam PBQs are released. CompTIA provides one generic sample, and training resources offer realistic practice simulations. PBQs vary by exam form, but common types include firewall configs, log analysis, network diagrams, and wireless setup.
Should I do PBQs first or last?
There’s no single best strategy:
Some do PBQs first, then MCQs
Others skip PBQs, finish MCQs, then return
A hybrid approach (do easy PBQs, skip hard ones) works well
The key is having a deliberate plan and watching the clock.
Do PBQs involve hacking tools like Metasploit?
No. Security+ PBQs stay entry-level. You may interpret outputs (e.g., Nmap results or logs), but you won’t run advanced exploitation tools. Think junior security administrator, not penetration tester.
What if a PBQ simulation glitches?
Notify the proctor immediately. PBQs are meant to be technically simple. Also take time to understand each interface—some confusion is just unfamiliar UI, not a real error.
Are PBQs the same for every test-taker?
No. PBQs are pulled from a question pool and change over time. While PBQ types stay consistent, the specific scenarios vary. This is why skill-based prep matters more than memorization.
Does skipping a PBQ hurt my score?
Skipping itself does not—but leaving it unanswered does. If time is short, even a partial attempt is better than leaving it blank.
How can I practice PBQs legitimately (no dumps)?
Best options include:
Official CompTIA samples and CertMaster Labs
Reputable books/courses with PBQ-style exercises
Online labs aligned to SY0-701 objectives
Home labs (firewalls, logs, wireless configs)
Community-created conceptual scenarios (not real exam content)
13. Final Thoughts: Turning PBQs into a Strength
PBQs are not designed to trick you.
They reward:
Structured thinking
Calm analysis
Practical security reasoning
If you prepare for patterns instead of questions, PBQs become one of the most reliable scoring opportunities on the Security+ exam.
